| Study | In-vitro |
| Purpose |
To measure the ginsenoside transforming activity of human intestinal microbial flora |
| X axis |
Left : Ginsenoside Rb1 treatment Right : Ginseng extract treatment |
| Y axis | Ginsenoside transforming activity of microbial flora |
| Study | Clinical pharmacokinetics |
| Purpose |
To measure the intestinal absorption of ginseng extract |
| X axis | Blood sampling time |
| Y axis | Plasma concentration of compound K (analytical marker of the final metabolite of ginsenoside) |
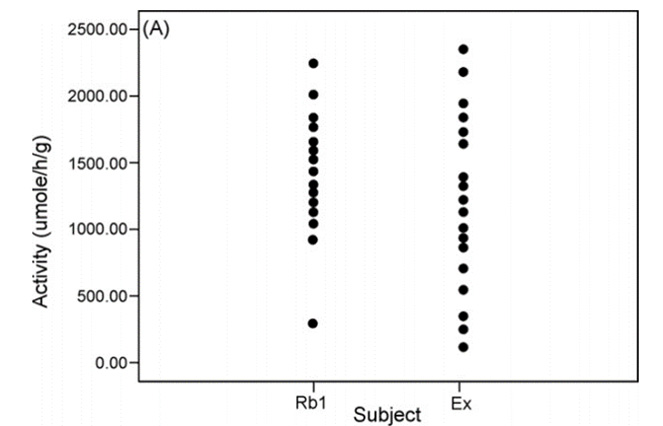 Ginsenoside transforming activity of
intestinal microbial flora
differs between individuals.
Ginsenoside transforming activity of
intestinal microbial flora
differs between individuals.
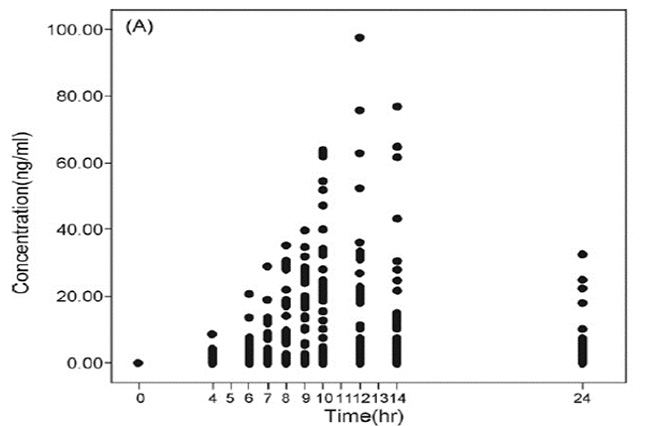 The absorption rate of Compound K
differs between individuals due to
differences in intestinal microbial flora.
The absorption rate of Compound K
differs between individuals due to
differences in intestinal microbial flora.
* Ref. Lee J. et al., J. Ethnopharmacol., 2009, 122(1):143-148

Dietary habits

Genetic background

Intestinal microbiome condition
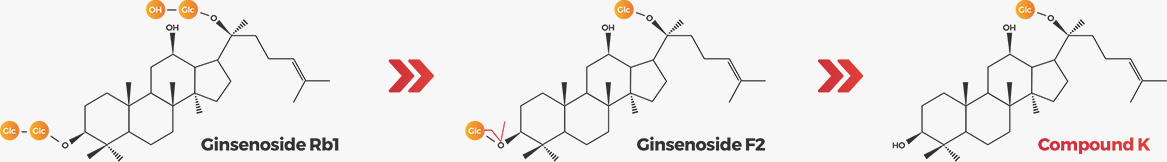
Most ginsenoside compounds come with relatively higher molecular weight
when extracted by conventional methods and
they could not be absorbed into the body depending on individuals.
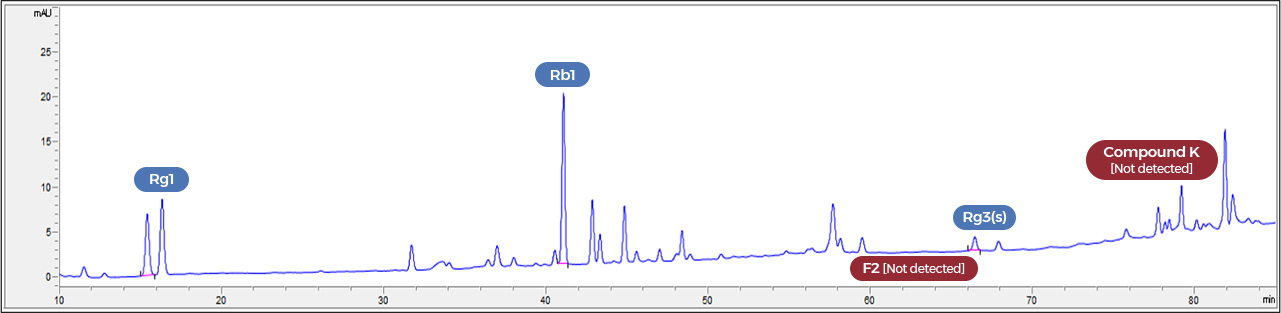 Before fermentation
Before fermentation
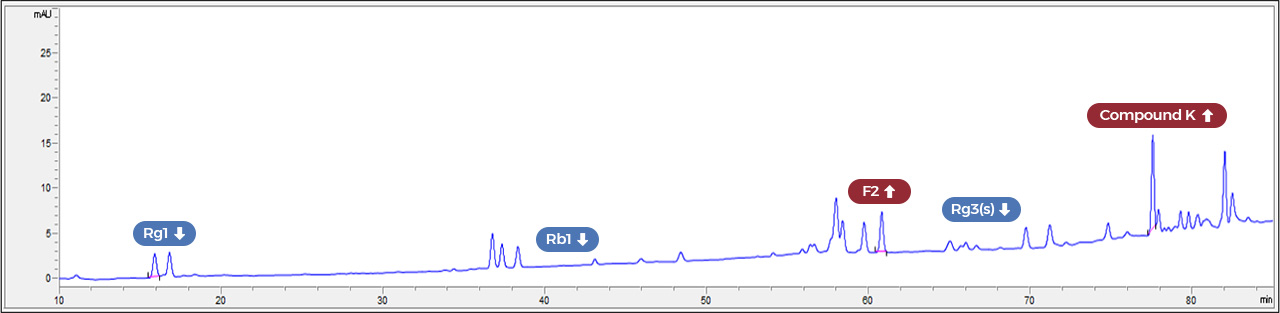 After fermentation
After fermentation
At every single batch, we make sure of the presence of specific marker ginsenosides
that are created by the fermentation method.
| Daily Dose | Trial Period | Participants | Design |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 g | 24 hours | 13 healthy males | Double-blind, randomized, crossover |
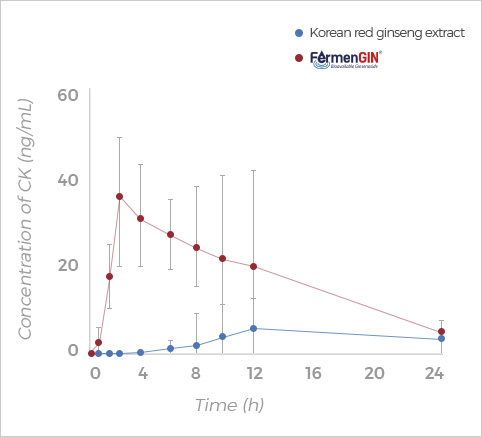
Compound K
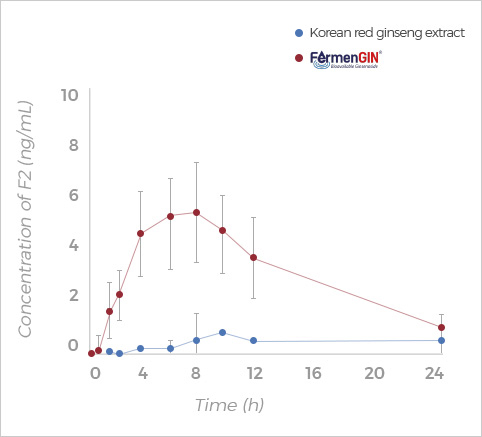
F2
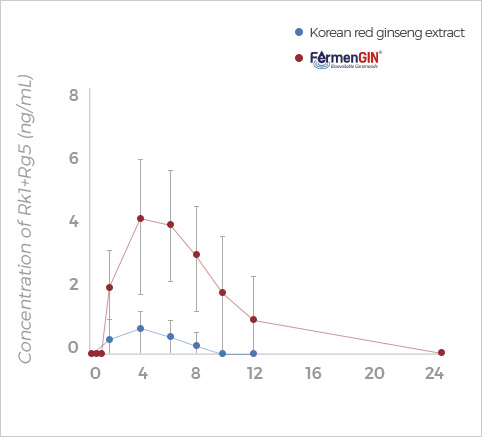
Rk1+Rg5
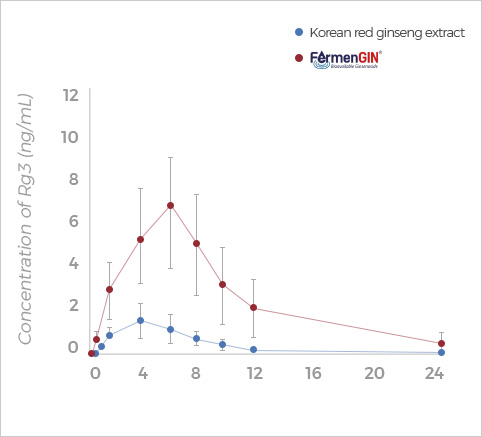
Rg3
Rg3, Rk1+Rg5, F2, and CK ginsenosides showed
higher Cmax, AUC(0-t), and AUC(0-∞) after oral administration of FermenGIN,
compared with red ginseng extract.
The significant increase in the AUC and Cmax of ginsenosides indicates that
FermenGIN ginsenosides were absorbed better than red ginseng extract.

| Test sample | Concentration | Panel |
|---|---|---|
| Normal red ginseng extract | 0.1% | 64 |
| FermenGIN | 0.1% |
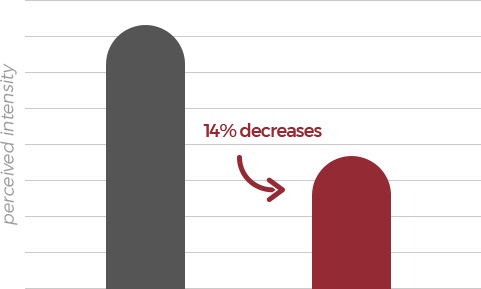
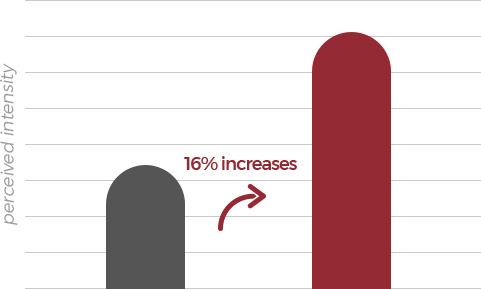
According to the statistical data of panel responses, it turned out FermenGIN is
less bitter by 14% and sweeter by 16% than normal red ginseng extract .